Stress has become one of the most significant health challenges of the 21st century. From demanding workplaces to social and personal pressures, many people find themselves constantly seeking relief from the relentless pace of modern life. Amid various tools and therapies, mindful meditation has emerged as a proven, practical technique for alleviating stress and promoting mental wellness.
Understanding Mindful Meditation
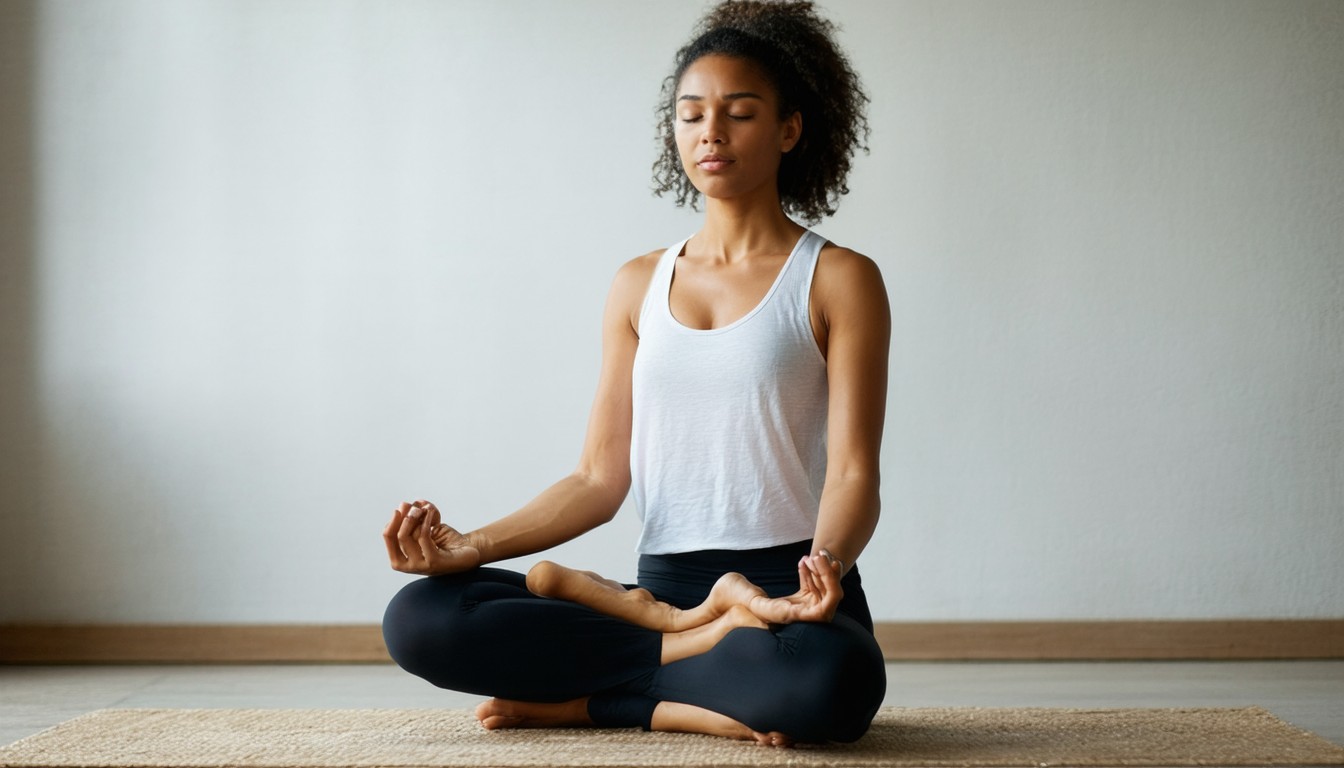
Mindful meditation is a mental practice rooted in ancient contemplative traditions, particularly in Buddhism, but widely adapted in clinical psychology and Western wellness culture over the past few decades. The core principle involves paying intentional, nonjudgmental attention to the present moment—observing sensations, thoughts, and emotions without getting caught up in them.
The Science Behind Mindful Meditation
In recent years, rigorous scientific research has provided mounting evidence for the positive effects of mindful meditation on stress reduction. Functional MRI scans and physiological studies reveal that regular meditators exhibit reduced activity in the amygdala, the brain’s stress and fear center, during stressful events.
A landmark meta-analysis published in JAMA Internal Medicine reviewed the effects of mindfulness meditation programs and found that these practices provide moderate evidence for reducing anxiety, depression, and pain. While the precise mechanisms are continually studied, experts agree on one thing: mindfulness helps disrupt the body’s habitual stress response.
“Mindfulness is not a magic bullet, but numerous randomized controlled trials show real, measurable benefits for stress, mood, and even certain physical health measures,” says Dr. Julia Samton, a board-certified psychiatrist and meditation teacher.
Key Benefits of Mindful Meditation for Stress Relief
Mindful meditation’s impact is far-reaching—not only does it reduce momentary feelings of stress, but it can also build long-term resilience. The following are some of the most well-documented benefits:
Emotional Regulation and Resilience
Practicing mindfulness cultivates an increased awareness of emotional triggers, allowing individuals to respond to challenges with greater composure. Instead of reacting impulsively, meditators often report a calmer, more measured approach to stressful situations—a skill that translates into all areas of life.
Lowered Physiological Indicators of Stress
Meditation practices have been associated with reductions in heart rate, blood pressure, and cortisol (the body’s primary stress hormone). According to findings from Harvard Medical School, participants who completed an eight-week mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) program displayed significant decreases in physiological stress markers.
Enhanced Focus and Cognitive Flexibility
Chronic stress can cloud judgment and diminish concentration. Mindful meditation, on the other hand, enhances cognitive clarity and the ability to focus. This increased mental agility helps people better manage the competing demands that often drive stress.
Improved Sleep Quality
Struggles with sleep are common among people experiencing stress. Several studies highlight that regular mindfulness meditation improves sleep quality—likely by calming the mind and reducing the intrusive thoughts that often keep people awake.
Practical Strategies for Integrating Mindful Meditation
Adopting meditation into daily life does not require an elaborate setup. Even brief, regular sessions can be effective. Here are some actionable approaches:
Setting Up a Meditation Practice
- Start Small: Begin with 5–10 minutes a day and gradually increase the duration.
- Choose a Comfortable Space: A quiet, non-distracting environment supports deeper focus.
- Use Guided Meditations: Apps like Headspace, Calm, and Insight Timer provide structured practices for all levels.
- Be Consistent: Schedule meditation at the same time daily to acquire the habit.
Mindfulness Techniques Beyond Sitting Meditation
Mindfulness extends beyond formal practice:
- Mindful Breathing: Focus attention on the rhythm of breath during daily activities.
- Body Scan: Systematically bring awareness to different body parts, noticing sensations.
- Walking Meditation: Attend to each step and the sensation of movement.
- Informal Mindfulness: Bring conscious attention to routine actions, such as eating or washing dishes.
In practice, many corporations have implemented mindfulness training as part of their employee wellness initiatives. For instance, companies like Google and General Mills report enhanced productivity and lower absenteeism among participants.
Addressing Common Obstacles and Misconceptions
Despite its accessible nature, some individuals struggle to establish a meditation habit. Typical barriers include the belief that meditation requires “emptying the mind,” or a lack of time. Experts emphasize that the goal is not to eliminate thoughts, but rather to notice them without becoming attached or judgmental.
For those feeling too busy, micro-practices—pausing for a single mindful breath before meetings or emails—can effectively weave mindfulness into even the most demanding schedules.
Mindful Meditation in Modern Healthcare
The increasing recognition of mindfulness by mainstream healthcare providers reflects its efficacy. Mindful-based programs are now routinely prescribed for a range of stress-related conditions, from chronic pain to generalized anxiety disorder, complementing traditional therapies.
The integration of mindfulness into cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and other modalities represents a trend toward holistic care, where mental, emotional, and physical factors are addressed as interconnected components of well-being.
Case Study: Mindfulness in Medical Settings
Hospitals such as the University of Massachusetts Medical Center have institutionalized mindfulness programs for patients and staff. Participants report reductions in perceived stress and improvements in overall quality of life, supporting the broader adoption of these strategies in healthcare systems worldwide.
Conclusion: Making Mindfulness a Sustainable Practice
Mindful meditation is a well-established, evidence-backed approach to managing stress and enhancing overall well-being. By training the mind to observe rather than react, individuals can shift their relationship to stress and foster deeper resilience. Whether integrated through brief daily practices or formal programs, mindfulness offers a sustainable antidote to the pressures of contemporary life.
For those seeking to reduce stress and improve mental health, incorporating even simple mindfulness practices can mark the beginning of a transformational journey.
FAQs
What is mindful meditation and how is it different from other types of meditation?
Mindful meditation focuses on being present and observing thoughts, emotions, and sensations with nonjudgmental awareness. Unlike some forms of meditation that aim to achieve specific states or focus on mantras, mindfulness emphasizes acceptance and presence in the current moment.
How long does it take to see results from mindful meditation for stress?
Many people notice positive changes within a few weeks of regular practice, often around 10–20 minutes daily. However, consistency over time typically yields the most noticeable and lasting benefits.
Can mindful meditation replace professional mental health care?
While mindfulness can be a powerful complement to therapy or medication, it shouldn’t replace professional medical advice for conditions like severe anxiety or depression. It is most effective as part of a holistic self-care or treatment plan.
Is it normal to have distracting thoughts during meditation?
Yes, wandering thoughts are a common part of meditation. The practice involves noticing these thoughts without judgment and gently bringing attention back to the chosen point of focus.
Are there any risks or downsides to practicing mindful meditation?
For most people, mindful meditation is safe and carries minimal risks. In rare cases, individuals with severe trauma or specific mental health conditions may experience uncomfortable emotions. Consulting a healthcare provider before beginning any new wellness practice is advisable if concerns arise.
How can I make mindful meditation a regular habit?
Set a specific time and place for daily practice, use reminders, and start with short, manageable sessions. Joining a group or using guided resources can also provide structure and motivation.








Leave a comment